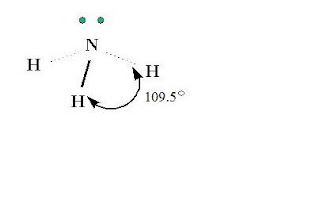
Ammonia is a molecule, which is a combination of nitrogen and hydrogen. Ammonia has the formula of NH3. Nitrogen is the central atom and has five valence electrons. Hydrogen has one valence electron. Each of the three hydrogen atoms share its electrons with nitrogen to form a covalent bond. Nitrogen has two left over electrons that do not bond.
3-D Structure of Ammonia
- shape: AX3E (triangular pyramid)
- angles: 109.5 degrees

Image Sources:
http://newenergyandfuel.com/http:/newenergyandfuel/com/2008/09/30/a-fast-way-out-of-using-gasoline/nh3/